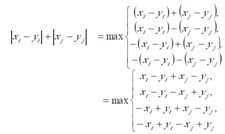The WSAEventSelect function specifies an event object to be associated with the specified set of FD_XXX network events.
确定与所提供的FD_XXX网络事件集合相关的一个事件对象。
Syntax
int WSAEventSelect( __in SOCKET s, __in WSAEVENT hEventObject, __in long lNetworkEvents );
Parameters
-
s [in]
-
Descriptor identifying the socket.
hEventObject [in]
-
Handle identifying the event object to be associated with the specified set of FD_XXX network events.
lNetworkEvents [in]
-
Bitmask that specifies the combination of FD_XXX network events in which the application has interest.
Return Value
The return value is zero if the application's specification of the network events and the associated event object was successful. Otherwise, the value SOCKET_ERROR is returned, and a specific error number can be retrieved by calling WSAGetLastError.
As in the case of the select and WSAAsyncSelect functions, WSAEventSelect will frequently be used to determine when a data transfer operation (send or recv) can be issued with the expectation of immediate success. Nevertheless, a robust application must be prepared for the possibility that the event object is set and it issues a Windows Sockets call that returns WSAEWOULDBLOCK immediately. For example, the following sequence of operations is possible:
- Data arrives on socket s; Windows Sockets sets the WSAEventSelect event object.
- The application does some other processing.
- While processing, the application issues an ioctlsocket(s, FIONREAD...) and notices that there is data ready to be read.
- The application issues a recv(s,...) to read the data.
- The application eventually waits on the event object specified in WSAEventSelect, which returns immediately indicating that data is ready to read.
- The application issues recv(s,...), which fails with the error WSAEWOULDBLOCK.
Having successfully recorded the occurrence of the network event (by setting the corresponding bit in the internal network event record) and signaled the associated event object, no further actions are taken for that network event until the application makes the function call that implicitly reenables the setting of that network event and signaling of the associated event object.
| Network event | Re-enabling function |
|---|---|
| recv, recvfrom, WSARecv, or WSARecvFrom. |
| send, sendto, WSASend, or WSASendTo. |
| recv, recvfrom, WSARecv, or WSARecvFrom. |
| accept or WSAAccept unless the error code returned is WSATRY_AGAIN indicating that the condition function returned CF_DEFER. |
| None. |
| None. |
| WSAIoctl with command SIO_GET_QOS. |
| Reserved. |
| WSAIoctl with command SIO_ROUTING_INTERFACE_CHANGE. |
| WSAIoctl with command SIO_ADDRESS_LIST_CHANGE. |
Any call to the reenabling routine, even one that fails, results in reenabling of recording and signaling for the relevant network event and event object.
For FD_READ, FD_OOB, and FD_ACCEPT network events, network event recording and event object signaling are level-triggered. This means that if the reenabling routine is called and the relevant network condition is still valid after the call, the network event is recorded and the associated event object is set. This allows an application to be event-driven and not be concerned with the amount of data that arrives at any one time. Consider the following sequence:
- Transport provider receives 100 bytes of data on socket s and causes WS2_32.DLL to record the FD_READ network event and set the associated event object.
- The application issues recv(s, buffptr, 50, 0) to read 50 bytes.
- The transport provider causes WS2_32.DLL to record the FD_READ network event and sets the associated event object again since there is still data to be read.
With these semantics, an application need not read all available data in response to an FD_READ network event—a single recv in response to each FD_READ network event is appropriate.
The FD_QOS event is considered edge triggered. A message will be posted exactly once when a quality of service change occurs. Further messages will not be forthcoming until either the provider detects a further change in quality of service or the application renegotiates the quality of service for the socket.
The FD_ROUTING_INTERFACE_CHANGE and FD_ADDRESS_LIST_CHANGE events are considered edge triggered as well. A message will be posted exactly once when a change occurs after the application has requested the notification by issuing WSAIoctl with SIO_ROUTING_INTERFACE_CHANGE or SIO_ADDRESS_LIST_CHANGE correspondingly. Other messages will not be forthcoming until the application reissues the IOCTL and another change is detected since the IOCTL has been issued.
If a network event has already happened when the application calls WSAEventSelect or when the reenabling function is called, then a network event is recorded and the associated event object is set as appropriate. For example, consider the following sequence:
- An application calls listen.
- A connect request is received but not yet accepted.
- The application calls WSAEventSelect specifying that it is interested in the FD_ACCEPT network event for the socket. Due to the persistence of network events, Windows Sockets records the FD_ACCEPT network event and sets the associated event object immediately.
The FD_WRITE network event is handled slightly differently. An FD_WRITE network event is recorded when a socket is first connected with connect/ WSAConnect or accepted with accept/ WSAAccept, and then after a send fails with WSAEWOULDBLOCK and buffer space becomes available. Therefore, an application can assume that sends are possible starting from the first FD_WRITE network event setting and lasting until a send returns WSAEWOULDBLOCK. After such a failure the application will find out that sends are again possible when an FD_WRITE network event is recorded and the associated event object is set.
The FD_OOB network event is used only when a socket is configured to receive OOB data separately. If the socket is configured to receive OOB data inline, the OOB (expedited) data is treated as normal data and the application should register an interest in, and will get FD_READ network event, not FD_OOB network event. An application can set or inspect the way in which OOB data is to be handled by using setsockopt or getsockopt for the SO_OOBINLINE option.
The error code in an FD_CLOSE network event indicates whether the socket close was graceful or abortive. If the error code is zero, then the close was graceful; if the error code is WSAECONNRESET, then the socket's virtual circuit was reset. This only applies to connection-oriented sockets such as SOCK_STREAM.
The FD_CLOSE network event is recorded when a close indication is received for the virtual circuit corresponding to the socket. In TCP terms, this means that the FD_CLOSE is recorded when the connection goes into the TIME WAIT or CLOSE WAIT states. This results from the remote end performing a shutdown on the send side or a closesocket. FD_CLOSE being posted after all data is read from a socket. An application should check for remaining data upon receipt of FD_CLOSE to avoid any possibility of losing data.
Note that Windows Sockets will record only an FD_CLOSE network event to indicate closure of a virtual circuit. It will not record an FD_READ network event to indicate this condition.
The FD_QOS or FD_GROUP_QOS network event is recorded when any parameter in the flow specification associated with socket s. Applications should use WSAIoctl with command SIO_GET_QOS to get the current quality of service for socket s.
The FD_ROUTING_INTERFACE_CHANGE network event is recorded when the local interface that should be used to reach the destination specified in WSAIoctl with SIO_ROUTING_INTERFACE_CHANGE changes after such IOCTL has been issued.
The FD_ADDRESS_LIST_CHANGE network event is recorded when the list of addresses of protocol family for the socket to which the application can bind changes after WSAIoctl with SIO_ADDRESS_LIST_CHANGE has been issued.
| Error code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| WSANOTINITIALISED | A successful WSAStartup call must occur before using this function. |
| WSAENETDOWN | The network subsystem has failed. |
| WSAEINVAL | One of the specified parameters was invalid, or the specified socket is in an invalid state. |
| WSAEINPROGRESS | A blocking Windows Sockets 1.1 call is in progress, or the service provider is still processing a callback function. |
| WSAENOTSOCK | The descriptor is not a socket. |
Remarks
The WSAEventSelect function is used to specify an event object, hEventObject, to be associated with the selected FD_XXX network events, lNetworkEvents. The socket for which an event object is specified is identified by the s parameter. The event object is set when any of the nominated network events occur.
The WSAEventSelect function operates very similarly to WSAAsyncSelect, the difference being the actions taken when a nominated network event occurs. The WSAAsyncSelect function causes an application-specified Windows message to be posted. The WSAEventSelect sets the associated event object and records the occurrence of this event in an internal network event record. An application can use WSAWaitForMultipleEvents to wait or poll on the event object, and use WSAEnumNetworkEvents to retrieve the contents of the internal network event record and thus determine which of the nominated network events have occurred.
WSAEventSelect is the only function that causes network activity and errors to be recorded and retrievable through WSAEnumNetworkEvents. See the descriptions of select and WSAAsyncSelect to find out how those functions report network activity and errors.
The WSAEventSelect function automatically sets socket s to nonblocking mode, regardless of the value of lNetworkEvents. To set socket s back to blocking mode, it is first necessary to clear the event record associated with socket s via a call to WSAEventSelect with lNetworkEvents set to zero and the hEventObject parameter set to NULL. You can then call ioctlsocket or WSAIoctl to set the socket back to blocking mode.
The lNetworkEvents parameter is constructed by using the bitwise OR operator with any of the values specified in the following list.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| FD_READ | Wants to receive notification of readiness for reading. |
| FD_WRITE | Wants to receive notification of readiness for writing. |
| FD_OOB | Wants to receive notification of the arrival of OOB data. |
| FD_ACCEPT | Wants to receive notification of incoming connections. |
| FD_CONNECT | Wants to receive notification of completed connection or multipoint join operation. |
| FD_CLOSE | Wants to receive notification of socket closure. |
| FD_QOS | Wants to receive notification of socket (QOS changes. |
| FD_GROUP_QOS | Reserved for future use with socket groups. Want to receive notification of socket group QOS changes. |
| FD_ROUTING_ INTERFACE_CHANGE | Wants to receive notification of routing interface changes for the specified destination. |
| FD_ADDRESS_ LIST_CHANGE | Wants to receive notification of local address list changes for the address family of the socket. |
Issuing a WSAEventSelect for a socket cancels any previous WSAAsyncSelect or WSAEventSelect for the same socket and clears the internal network event record. For example, to associate an event object with both reading and writing network events, the application must call WSAEventSelect with both FD_READ and FD_WRITE, as follows:
rc = WSAEventSelect(s, hEventObject, FD_READ|FD_WRITE);
It is not possible to specify different event objects for different network events. The following code will not work; the second call will cancel the effects of the first, and only the FD_WRITE network event will be associated with hEventObject2:
rc = WSAEventSelect(s, hEventObject1, FD_READ); rc = WSAEventSelect(s, hEventObject2, FD_WRITE); //bad
To cancel the association and selection of network events on a socket, lNetworkEvents should be set to zero, in which case the hEventObject parameter will be ignored.
rc = WSAEventSelect(s, hEventObject, 0);
Closing a socket with closesocket also cancels the association and selection of network events specified in WSAEventSelect for the socket. The application, however, still must call WSACloseEvent to explicitly close the event object and free any resources.
The socket created when the accept function is called has the same properties as the listening socket used to accept it. Any WSAEventSelect association and network events selection set for the listening socket apply to the accepted socket. For example, if a listening socket has WSAEventSelect association of hEventObject with FD_ACCEPT, FD_READ, and FD_WRITE, then any socket accepted on that listening socket will also have FD_ACCEPT, FD_READ, and FD_WRITE network events associated with the same hEventObject. If a different hEventObject or network events are desired, the application should call WSAEventSelect, passing the accepted socket and the desired new information.
Example Code
The following example demonstrates the use of the WSAEventSelect function.
//-------------------------
// Declare and initialize variables
SOCKET ListenSocket;
WSAEVENT NewEvent;
sockaddr_in InetAddr;
//-------------------------
// Initialize listening socket
ListenSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
//-------------------------
// Bind listening socket
InetAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
InetAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
InetAddr.sin_port = htons(27015);
bind (ListenSocket, (SOCKADDR *) &InetAddr, sizeof(InetAddr));
//-------------------------
// Create new event
NewEvent = WSACreateEvent();
//-------------------------
// Associate event types FD_ACCEPT and FD_CLOSE
// with the listening socket and NewEvent
WSAEventSelect( ListenSocket, NewEvent, FD_ACCEPT | FD_CLOSE);
//----------------------
// Listen for incoming connection requests
// on the created socket
if (listen( ListenSocket, SOMAXCONN ) == SOCKET_ERROR)
printf("Error listening on socket./n");
printf("Listening on socket.../n");
// Need an event handler added to handle connection requests
Requirements
| Minimum supported client | Windows 2000 Professional |
|---|---|
| Minimum supported server | Windows 2000 Server |
| Header | Winsock2.h |
| Library | Ws2_32.lib |
| DLL | Ws2_32.dll |